Lab 7
Introduction
Photogrammetry is the science of making accurate measurements from aerial photographs and satellite images and in the process obtain geometrically reliable products. The goal of this lab was to develop skills in performing photogrammetric tasks on aerial photographs and satellite images. What will be keyed on in this lab is the mathematics behind the calculation of photographic scales, measurement of areas and perimeters of features, and calculating relief displacement.
This lab deals with the introduction of stereoscopy and performing orthorectification on satellite images. All in all this lab is really meant to put us in the position to perform diverse photogrammetric tasks.
Methods
Part 1
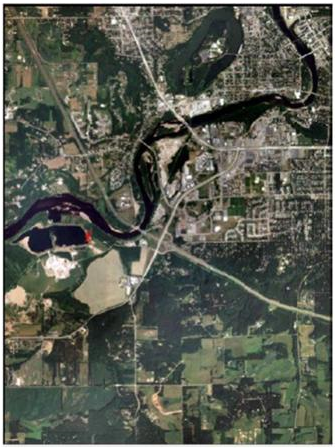
There are two tasks located in this first section. The first deals with calculating scale of nearly vertical aerial photographs. In this section we were to open up the image Eau Claire_West-se.jpg. In this image there are two points, labeled A and B. The task was to calculate the scale of this aerial photograph by using a ruler and measuring the distance on the computer screen. The only information that was given was the actual ground distance between the two points is 8822.47 ft. The image that was used for this section can be seen below in Figure 1.
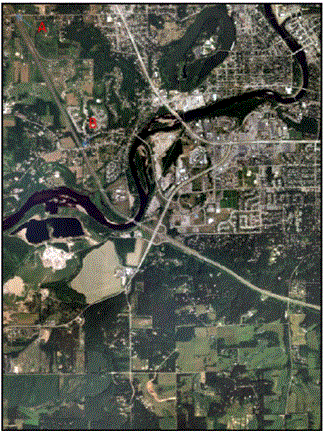 |
| Figure 1: This is the image that was used to complete section 1. The points A and B are located in the Northwestern portion of the image. Image created by: Cyril Wilson |
The second task in this section also deals with scale. Now the image ec_east-sw.img will be used. This image was taken by the National Agriculture Imagery Program (NAIP) in 2005. This aircraft acquired the photograph at an altitude of 20,000 ft. above sea level with a camera that had a focal length lens of 152 mm. One other bit of information given was that Eau Claire County is 796 ft. in elevation. The task is to use this information to figure out the scale. Looking at the image for this task isn't really necessary, it is more mathematical based.
Section 2
This section deals with measurement of areas of features on aerial photographs. This begins by displaying the image ec_west-se.img in an ERDAS viewer. The idea behind this section is to trace the feature located in Figure 2 and then look at the measurement window to obtain the area and perimeter of the feature.
These are the instructions as to obtaining the measurements.
- Click the 'Measure' icon. This will change the tool panel, shown below.
- On the tool panel, click on show Panel (arrow A). This will open a View Measurements table at the bottom of the image.
- Click a Point drop down arrow (arrow B) to show various measurement tools.
- Click on the Polygon tool (arrow C) to measure the area.
- Use that tool carefully to digitize the outline of the lagoon in the photo above. The area can be read directly from the Measurement window. Click the drop down default hectares to change to other units of measuring area and perimeter.
- Click on the Polyline tool (arrow D) to measure perimeter. Follow the same process as measuring the area.
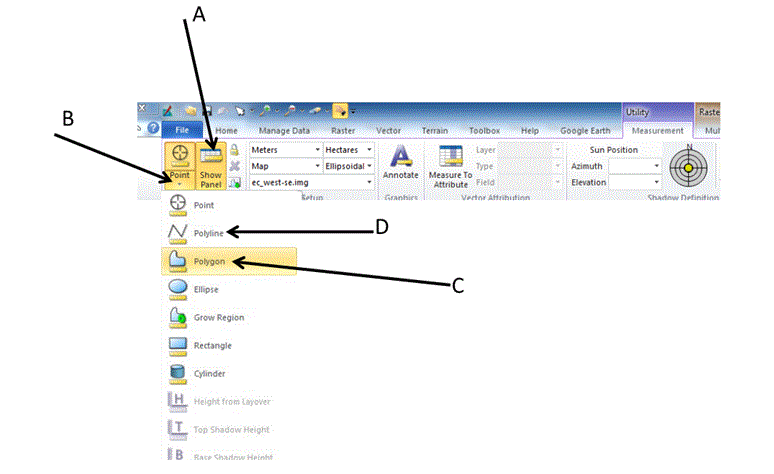 |
| Figure 3: This is an image of the tools that are needed to complete this section Image created by: Cyril Wilson |
Section 3
This section deals with calculating relief displacement from object height. The image used for this portion is ec_west-se.img, which can be seen below. The information given for this section is as follows; the height of the aerial camera above datum is 3,980 ft., the scale of the image is 1:3,209. Then a hint was given (hint: using a ruler to measure the height of the smoke stack and find its real world height; then measure the radial distance between the principal point and the top of the smoke stack). With data the relief displacement could then be calculated.
Part 2
This part of the lab deals with stereoscopy. To begin, the image ec_city.img needs to be brought into a viewer in ERDAS. Then open a second viewer and bring in the image ec_dem2.img. Then click on Terrain - Anaglyph to open the Anaglyph Generation window. In the Input DEM, input ec_dem2.img. For the Input image, input ec_city.img. In the Output image, insert the image ec_anaglyph.img located in the Steroscopy_output folder. Increase the vertical exaggeration to 2. Then click OK to run the model.
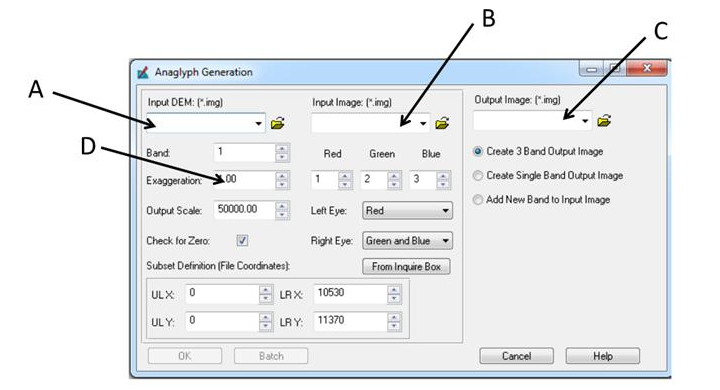 |
| Figure 5: This is the Anaglyph Generation window where the above operations are completed. Image created by: Cyril Wilson |
The final step is to use polaroid glasses to observe the image.
Part 3
This part deals with orthorectification. Erdas Imagine Lecia Photogrammetric Suite (LPS) will now be introduced. It is used in digital photogrammetry for triangulation, orthorectification of images collected by various sensors, extraction of digital surface and elevation models.
Tasks
- Create a new project.
- Select a horizontal reference source.
- Collect GCPs.
- Ass a second image to the block file.
- Collect GCPs in the second image.
- Perform sutomatic tie point collection.
- Triangulate the images.
- Orthorectify the images.
- View the orthoimages.
- Save the block file.
Section 1
The task of creating a new project is what section 1 deals with. Open up ERDAS and open the LPS Project Manager tool. Click the Create New Block File to open the Create New Block File dialog. Then navigate to the subfolder that was created for this lab and name the block file Sat_ortho, then click OK. The Model Setup dialog is now open. This is shown below in Figure 6.
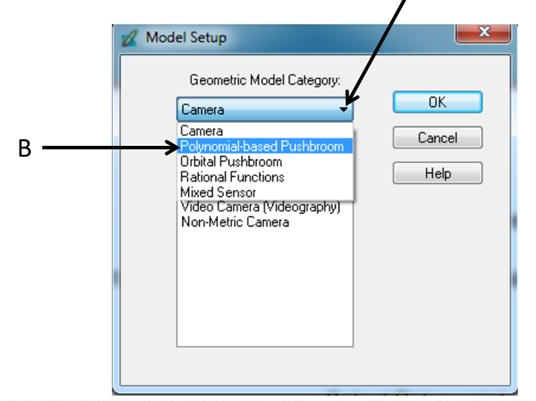 |
| Figure 6: This is a screenshot of the window that was opened in the previous steps. Image created by: Cyril Wilson |
Click on the Geometric Model Category and choose Polynomial-based Pushbroom. In the Geometric Model Category select SPOT Pushbroom, then click OK.
The Block Property Setup dialog is now open. Click Set in the Horizontal Reference Coordinate System. The Projection Chooser dialog is now open. In the Custom tab click Projection Type and choose UTM. Click the Spheroid Name and select Clarke 1866. Click the Datum Name and select NAD27(CONUS). Click UTM Zone field and type 11. Then click OK. Click OK on the Block Setup dialog to close it.
Section 2
This section deals with adding imagery to the Block and define the sensor model. In the Block Project Tree View click the Images folder. Then click the Add Frame icon, the Image File Name dialog is now open. Add the image Spot_pan.img, then click OK.
Next you will verify the parameters of the SPOT pushbroom sensor. Click the Show and Edit Frame Properties icon. Click Edit, the sensor information dialog is now displayed. Click OK and then click OK again.
Section 3
This section deals with activating the Point Measurement tool and collecting GCPs. Start by clicking the Start Point Measurement Tool and select the Classic Point Measurement Tool, then click OK. The Point Measurement tool opens displaying three views, a Main View, and two Cell Arrays.
Arrow A is the Main view, arrow B is the Tool Palette, arrow C is the Detail View, arrow D is Reference Cell Array, and arrow E is the File Cell Array. These are all shown in Figure 7 below.
Arrow A is the Main view, arrow B is the Tool Palette, arrow C is the Detail View, arrow D is Reference Cell Array, and arrow E is the File Cell Array. These are all shown in Figure 7 below.
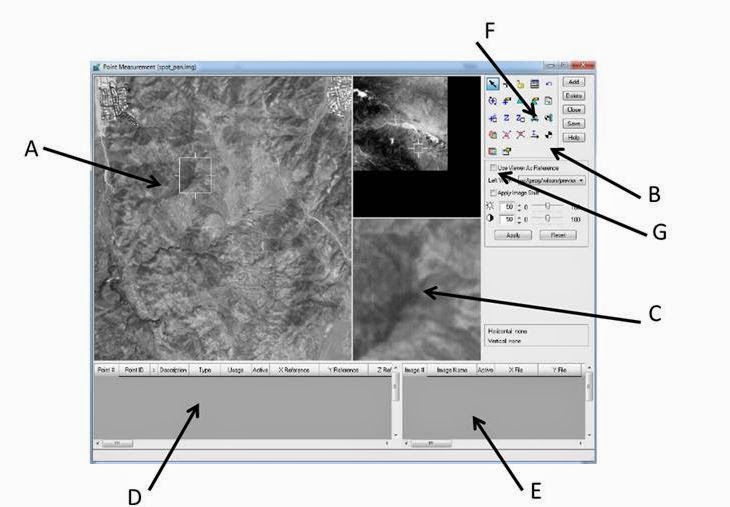 |
| Figure 7: This is a screenshot of the different views, tools, and arrays that will be used to complete this section of the lab. Image created by: Cyril Wilson |
In the Point Measurement tool palette, click the Reset horizontal reference source icon (F). The GCP Reference Source dialog is now open. In this check the Image Layer radio button. After clicking OK on the GCP Reference Source dialog, the Reference Image Layer dialog will now be open. Input the image xs_ortho.img. Click OK.
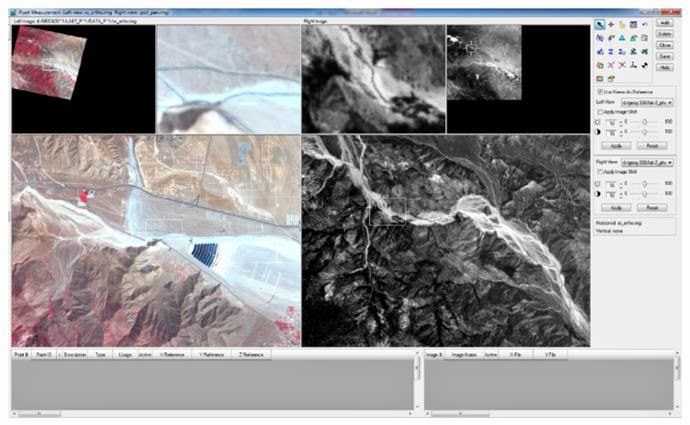
In the Point Measurement tool, click the checkbox next to Use Viewer As Reference (G). The Point Measurement tool automatically changes to display the reference image xs_ortho, in the left view of the point measurement tool, and the original image, spot_pan, in the right view. This can be seen below in Figure 8.
You will collect reference coordinates by selecting points in xs_ortho, the reference image that correspond to points in the block image, spot_pan. The following is the process of collecting these GCPs with helpful images.
Move the inquire box in the top left viewer showing the full extent of the xs_ortho image to where point ID 1 is (Shown in the Figure below). Click the Add button (A) in the Point Measurement tool. A row for Point ID 1 is added to the reference Cell Array. Move the inquire box in the lower left viewer containing the second view of the xs_ortho image, the detailed view also moves. Do this until you find the road intersectionin the detailed view, shown below.
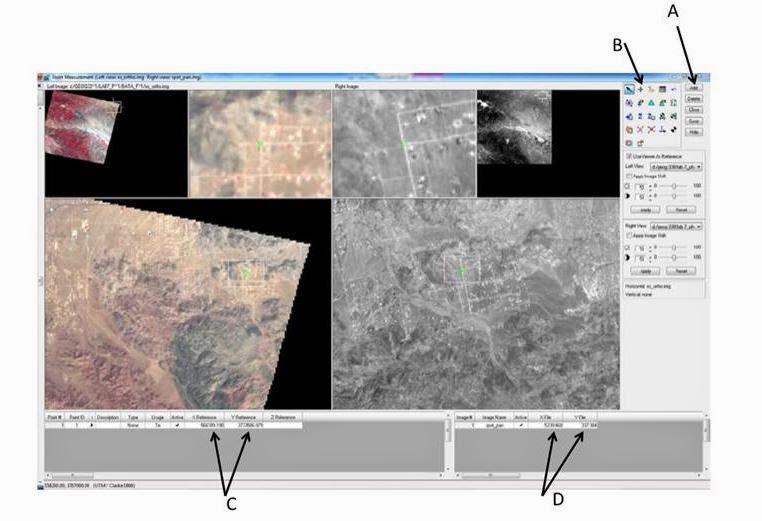 |
| Figure 9: This is a screenshot for the completion of the directions that are listed for this section. Image created by: Cyril Wilson |
Click the Create Point icon (B). Go to the Detail view on the xs_ortho image and click the road intersection, shown in green. Paint ID 1 is added to all three viewers containing the xs_ortho image. Check the reference control point coordinated; they should almost match those in the table below.
If the coordinates do not approximate (within 10 meters) of those listed in the table above, type in the correct coordinates from the table in the reference cell array, then press enter on the keyboard.
You will now collect the corresponding point on the block image, spot_pan.img. Check figure 1 for the location of Point ID 1 on the spot_pan image display in the right view of the point measurement tool. Move the inquire box in the views containing the spot_pan image until you see the road intersection. Click the Create Point icon and then click on the intersection. Check your spot_pan control point coordinates; they should approximate those in the table below.
If your coordinates do not approximate (within two pixels) those listed in the table above, then type in the correct coordinates in the file cell array, then press enter in your keyboard.
Click the Reset Horizontal Reference Source icon in the Point Measurement tool palette. This opens the GCP Reference Source dialog. Then check the Image Layer radio button. Click OK, opening the Reference Image Layer dialog. Input the image NAAP_2m-ortho.img. Click OK and the NAAP_2m-ortho.img is automatically loaded to the left viewer, shown below in Figure 10. To make the distinction between two different horizontal surfaces (xs_ortho and NAAP_2m-ortho) clearer, skip ID Point 10, and name the next control point Point ID 11.
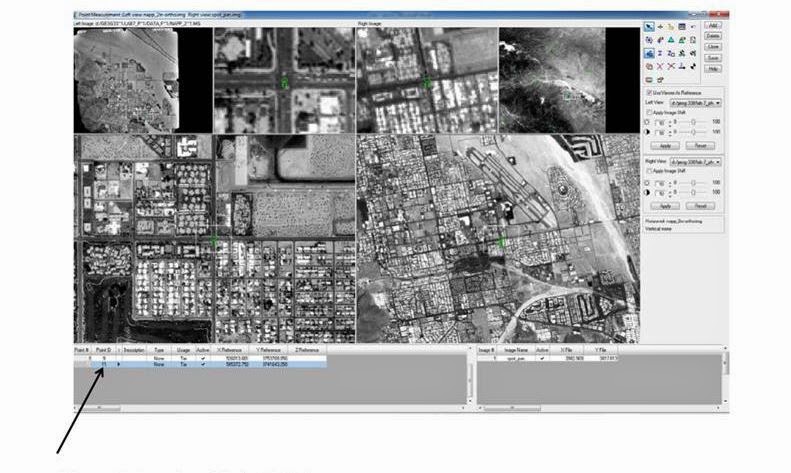 |
| Figure 10: This is a screenshot of the above process, showing the new images in the left-hand viewer. Image created by: Cyril Wilson |
The process for collecting the ID Points for 11 and 12 will be the same process that was used for points 1-9. When done, click Save and deselect the Use Viewer As Reference checkbox in the Point Measurement tool palette. Now only the spot_pan image will be shown.
You will not proceed to set the Vertical Reference Source and collect elevation information for all the horizontal reference GCPs you obtained from both images. The image palm_springs_dem.img will be used to collect the elevation information.
In the Point Measurement tool palette, click the Reset Vertical Reference Source icon. The Vertical Reference Source dialog then opens. Click the DEM radio button. Click the dropdown arrow and select Find DEM from the list. In the Add DEM File Name select the DEM palm_springs_dem.img., then click OK in the File Selector.
The DEM file selected displays in the DEM section of the Vertical Reference Source dialog. Click OK. Now right-click on the Point # column and Select All. Click the Update Z Values on Selected Points icon. The Z values of all reference points are updated in the reference cell array based on the values in the DEM selected. This can be seen in Figure 11 below.
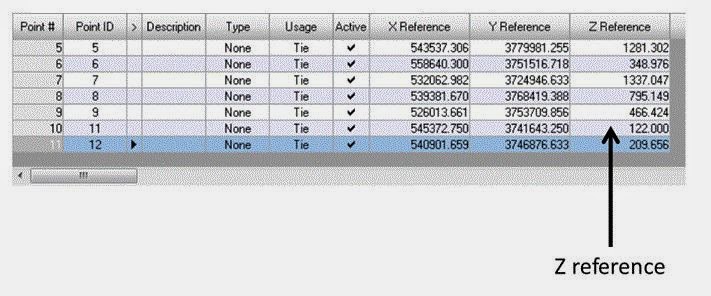 |
| Figure 11: This is a screenshot showing the newly acquired Z-values to display elevation for each of the control points. Image created by: Cyril Wilson |
Section 4
This section deals with set type and usage, with also adding a 2nd image to the block and collecting its GCPs. Left-click the title bar of the column titled Type to select the entire column. Right-click on Type to access the Column Options menu, then select Formula. The Formula dialog is not opened, shown below.
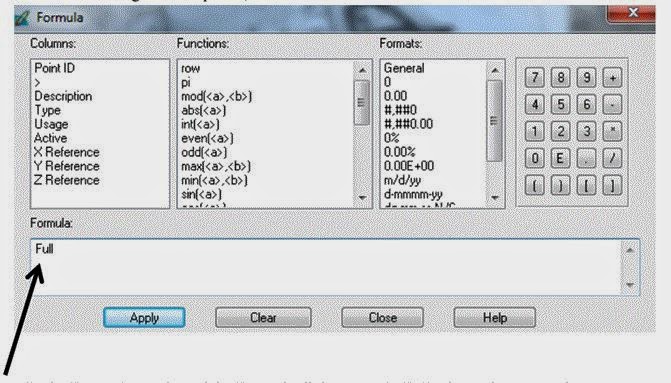 |
| Figure 12: This is a screenshot of the Formula dialog that will be used for this assignment. Image created by: Cyril Wilson |
In the Formula section type Full, then click Apply. Each Type entry now changes to indicate Full (X,Y, and Z coordinates). Repeat the above steps to update the Usage column to Control. The cell array should look exactly like the one below.
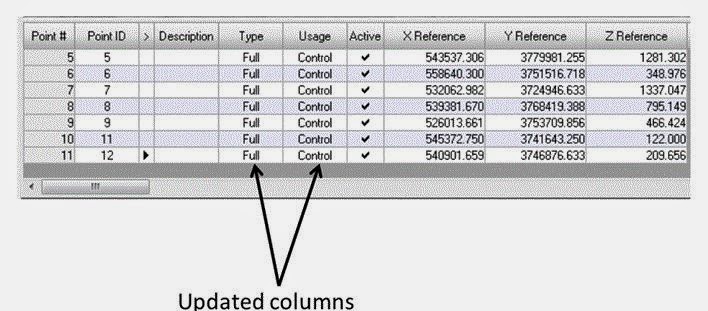 |
| Figure 13: This is a screenshot that shows the updated columns in the cell array. Image created by: Cyril Wilson |
In the Point Measurement tool, click Save. Then close the Point Management tool, you will be returned to LPS Project Manager.
Now that you have successfully finished the collection of reference coordinates from the xs_ortho and NAPP_2m-ortho, and file coordinated in the first block file, spot_pan, you can more on to the second image in the block, spot_panb.img.
Click the Add Frame icon and add the image spot_panb.img. Now click Row #2 to highlight the row corresponding to Image ID 2, spot_panb. Click Frame Properties icon. Click OK to accept original perimeters.
Click the Point measurement icon, select the Classic Point Measurement Tool, and click OK. Spot_panb will be displayed on the left while the initial image in the block spot_pan on the right. Points will be collected for Point ID #1, 2, 6, 8, 9, 12. This is done the exact same way that it was done in section 2. The reason some of the numbers are missing is because they are not located on spot_panb. When you're done click Save. The block interface should look like the image below in Figure 14.
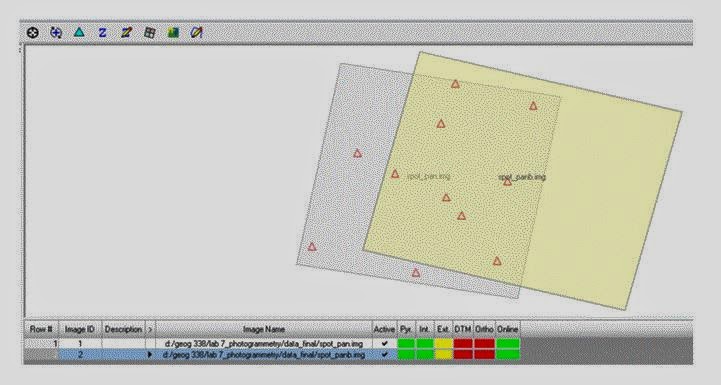 |
| Figure 14: This is a screenshot of what your Block Interface should look like after completing the steps above. Image created by: Cyril Wilson |
Section 5
This section deals with automatic tie points collection, triangulation, and ortho resampling. Begin by clicking the Automatic Tie Point Generation Properties. Image used radio button should be set to All Available. Initial Type radio button should be set to Exterior/Header/GCP. Check and confirm that the Image Layer Used for Computation is set to 1. Click the Distribution tab in the Automatic Tie Point Generation Properties dialog. In the Intended Number of Points/Image field, type in 40. Then click Run. Then click Save and close the Point Measurement tool.
In LPS Project Manager click on Edit-Triangulation Properties. Change the Iterations With Relaxation value to 3. Verify that the Image Coordinate Units for Report is set to Pixels. Click on the Point tab and in the Ground Point Type and Standard Deviations section click the Type dropdown and select Same Weighted Values. Change the values for the X, Y, and Z to 15. Then click Run. This will open a Triangulation Summary report, Figure 15.
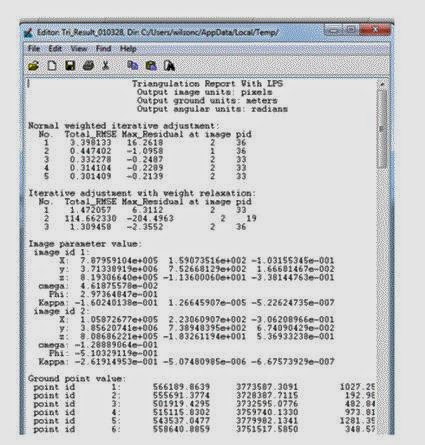 |
| Figure 15: This is a screenshot of what the Triangulation Summary report will look like. This is something that should be looked at and analyzed. Image created by: Cyril Wilson |
Click Accept and then OK. After returning to the LPS Project Manager click File-Save for the image that is created.
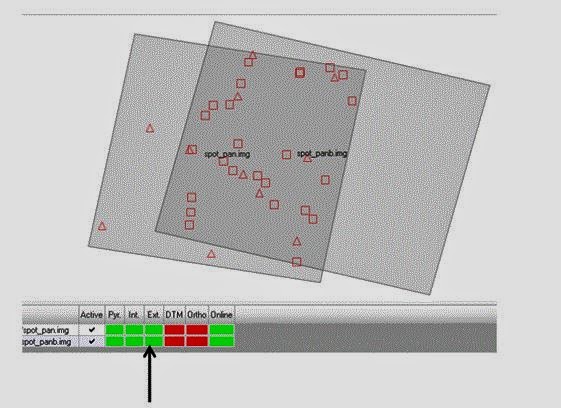 |
| Figure 16: This is a screenshot of what is produced through completing the above instructions. Image created by: Cyril Wilson |
Now click the Start Ortho Resampling Process. In the General Tab, click the DTM Source dropdown and select DEM. Click the DEM File Name dropdown and select Find DEM. Input the image palm_springs_dem.img. Click the Output Cell Sizes and change to 10.0. Click the Add button and make sure the second image in the block file spot_panb is in the Input File Name. Check the box to Use Current Cell Sizes, then click OK. Click OK in the Ortho Resampling dialog to start the process. After the model has run click File and Save.
Section 6
This last section just deals with viewing the Orthorectified Images. Just bring both the images into the frame and save the results.
Results
Section 1
1.
2 7/8 inches
1 inch = 3,000 ft
2.875” x 3,000’ = 8,625’
8,625’ x 12” = 103,500”
Scale = 1:103,500
2.
Altitude = 20,000 ft. elevation
= 796 ft. focal length lens =
152 mm. or 0.5 ft.
Scale = f / H – h
Scale = 0.5 / (20,000 – 796)
Scale = (0.5 / 19,204) x 2 =
Scale = 1:38,400
Section 2
3(a).
37.69 ha, 93.13 acres
3(b).
4175.79 m, 2.59 miles
Section 3
4.
D = h x r / H
Smoke stack = 0.5 inches scale
= 1:3,209 H = 3,980 ft.
3,209” x 0.5” = 1,604.5” / 12 = 133.7 ft.
Real world height = 133.7 ft.
Radial distance = 9.5” / 12 = 0.79’
D = (133.7 x 0.79) / 3,980
D = 0.027 x 12 = 0.32 inches
The feature must be plotted inwards 0.32 inches
Section 4
5.
From observing the anaglyph, it is apparent that there are
massive flood plains that stretch landward from the river. The elevation for
these land areas is fairly similar to that of the river. The area of lower
campus is located on that flood plain, and is the student housing area. The
student housing area, by Water Street, has a more decreasing elevation as it
reaches the river than that of the lower campus area. The difference between
the elevations of upper and lower campus are very apparent. The area where
Carson Park is located, being surrounded by Half Moon Lake, is at a higher
elevation than I would have expected. It is more elevated than both of the
previous areas that were talked about. The land located near the southern part
of the river in this image is at an extremely low elevation, almost matching
that of the river itself.
6.
I believe what I have described is very accurate to that of
reality. I’m not really sure about the southern portion of the river, but I do
know that the area of land located near the river on the student housing side
near Water Street experiences flooding every year in the spring. The sidewalks
are closed off because of this flooding. This is explained by the intense
decrease in elevation as you get closer to the river. There are some
differences, but they aren’t very noticeable because of the lack of flooding in
this part of the state.
7.
Like I said in the paragraph prior, this portion of the
state doesn’t exactly see much flooding. So in the anaglyph, it might show
lower elevations near the river that represent an outwash plain. But in reality
we never get that much flooding, so these elevations patterns can be seen as a
misconception. In the anaglyph you may think an area would receive a lot of
flooding because of the low elevation, but because of the portion of the state
we live in this is untrue.
It’s amazing how in the original city image of Eau Claire
the elevation differences are almost non-apparent, whereas the anaglyph image
the elevation differences jump off the page at you, literally.
Section 6
8.
I’m actually astounded at the accuracy of the spatial
overlap between these two images. I zoomed way in to the overlap area and there
is seemingly no difference; roads and rivers connect perfectly from one image
to another. When you zoom way in the obvious overlap of pixels is apparent, but
at a further distance out the overlap is unnoticeable. When you Fit To Frame
the overlap area is featured as a black line though, and when you are zoomed in
there is a slight difference in shading between the two images. But everything
matches up otherwise.